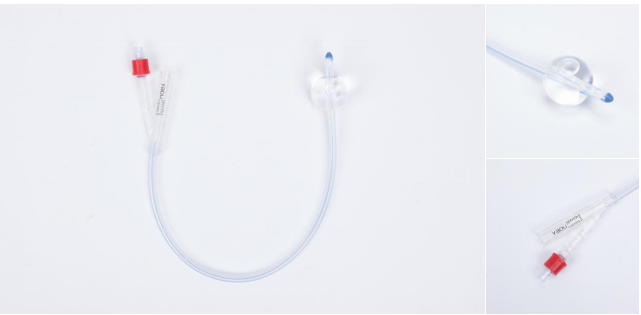
| Name: | Foley Catheter |
|---|---|
| Model No.: | Foley Catheters |
| Material: | silicone |
| Brand: | BESCO |
| Keywords: | Foley Catheters,Medical Foley Catheters,Disposable Medical Foley Catheters |
| LEAD TIME: | 5 days |
| Sample: | Available |
| MOQ: | 500 pcs |
| Payment Term: | T/T in advance |
| Country of Original: | China |
| Port: | Qingdao |
| Stock: | Available |
| Factory Address: | Changyuan,China |
| Office: | Zhengzhou,China |
Products Description
Completely inert for less tissue irritation and encrustation during extended periods of indwelling use
Easy insertion and less buckling with bullet-shaped tip
Features symmetrical balloon shape for improved reliability and larger inner lumen for better drainage
Clear for easy visualization of clots, mucous and urine flow
Radiopaque strip provides easy visualization during scans
Fr8,Fr12,Fr14,Fr8,Fr16,Fr18,Fr20,Fr22,Fr24
Balloon 10ml,30ml
Silicone
Not made with natural rubber latex
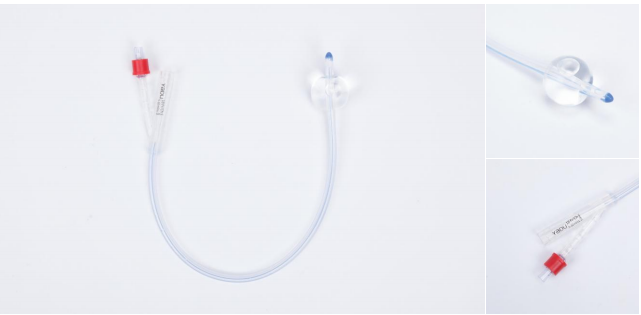
A Foley catheter, also known as an indwelling catheter, is a flexible tube inserted into the bladder to drain urine.
It's held in place by a balloon inflated with sterile water.
Foley catheters are used for various reasons, including urinary incontinence, retention, and during and after surgery
 Foley Catheters.png"/>
Foley Catheters.png"/>
A Foley catheter, or indwelling urinary catheter, is a thin, flexible tube inserted into the bladder through the urethra to drain urine when a person cannot urinate normally. A balloon on the catheter inflates with water to keep it securely in place, while the other end connects to a drainage bag to collect the urine. Foley catheters are used after surgery, during prolonged illness, or for chronic conditions like urinary retention or incontinence.
How it Works?
1. Insertion:
A healthcare provider inserts the thin, flexible tube through the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body) and into the bladder.
2. Balloon Inflation:
Once the tube is in the bladder, a small balloon at its tip is inflated with sterile water to hold the catheter in position.
3. Urine Drainage:
Urine then drains from the bladder through the catheter and into a connected drainage bag.
Why It's Used
Urinary Retention: When the bladder cannot empty itself.
Urinary Incontinence: To manage severe cases that cannot be controlled by other means.
Surgery: To assist bladder function during and after certain surgical procedures.
Medical Conditions: To manage conditions that make normal urination difficult.
Key Components
Catheter: The flexible tube that goes into the bladder.
Balloon: A small, inflatable balloon that secures the catheter in the bladder.
Drainage Tube: The part of the catheter that carries urine to the collection bag.
Drainage Bag: A reservoir, often worn on the leg, that collects the urine.
Important Considerations
Hygiene: Good hygiene is crucial to prevent infection while a catheter is in place.
Infection Risk: The longer a Foley catheter is in use, the higher the risk of a urinary tract infection.
Care: Healthcare providers teach patients and caregivers how to properly clean and care for the catheter and drainage system.